Nginx简介
0 条评论本来nginx应该是运维的活,但无奈公司运维没那么靠谱。只能多学点东西,nginx开发环境的简单配置还是要稍微了解一下,特此做个简单的记录
1. nginx常用指令
nginx查看版本号
nginx -v
nginx启动命令
nginx
nginx关闭命令
nginx -s stop
检查配置文件
nginx -t
重新加载配置文件
nginx -s reload
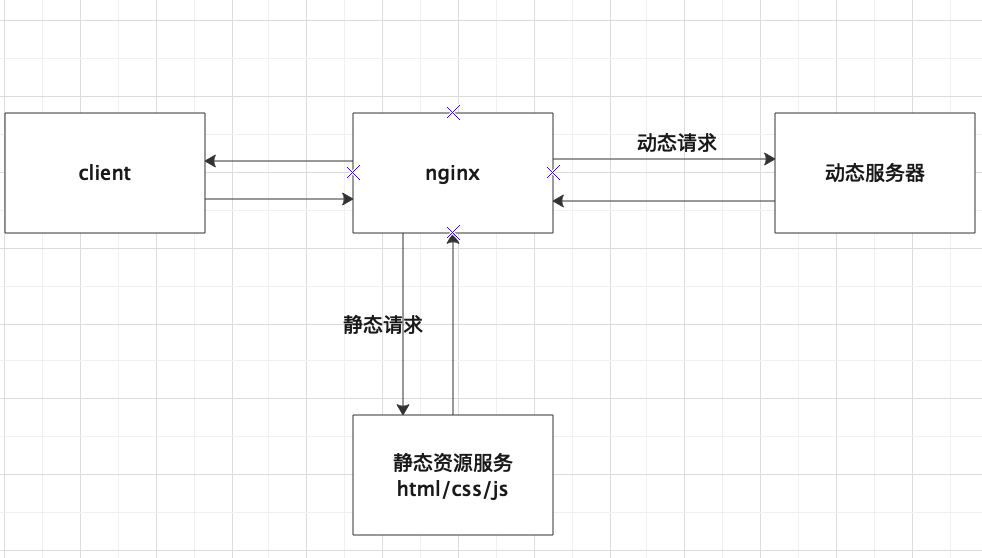
2. nginx配置文件(nginx.conf)
nginx配置文件有三个模块组成,分别是全局模块,event模块以及http模块
全局模块(主要设置nginx服务器整体运行的指令)
正常运行配置
user $username; //指定运行worker进程的用户和组;
pid /path/to/pid_file; //指定nginx守护进程的pid文件
worker_rlimit_nofile NUMBER; //设置所有worker进程最大可以打开的文件数,默认为1024;
worker_rlimit_core SIZE; //指明所有worker进程所能够使用的总体的最大核心文件大小,保持默认即可调试配置
daemon {on|off}; //是否已守护进程运行进程nginx,调试时应设置为off
master_process {on|off}; //是否以master/worker模型来运行nginx,调试时可以设置为off
error_log $path; //配置错误日志性能优化配置
worker_processse auto; //启动N个worker进程,这里的N为了避免上下文切换,通常设置为cpu总核数-1或等于总t核数
time_resolution INTERVAL; //计时器解析度。降低此值,可减少gettimeofday()系统调用的次数
worker_priority NUMBER; //指明worker进程的NICE值(优先级)event模块(events模块主要影响nginx服务器与用户的网络连接)
use epoll; //多路复用I/O中的一种方式,仅用于linux2.6以上内核,大大提升nginx性能
accept_mutex {on|off}; //master调度用户请求至各worker进程时使用的负载均衡锁,“on”表示能让多个worker轮流地、序列化地去响应新请求
lock_file FILE; //accept_nutex用到的互斥锁锁文件路径
use [epoll | rtsig | select | poll]; //指明使用的事件模型,建议让nginx自行选择
worker_connections 1024; //每个进程能够接受的最大连接数
multi_accept on; //尽可能多的接受请求http模块(web服务相关配置)
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20http { ## 协议级别
include mime.types;
default_type application/octet-stream;
keepalive_timeout 65;
gzip on;
sendfile on;##指定nginx是否调用sendfile函数(zero copy)来输出文件,对于普通应用必须设为on;
##如果用来进行下载等应用磁盘I/O重负载应用,可设置为OFF,以平衡磁盘与网络I/O处理速度,降低系统的uptime
autoindex on; ##开启目录列表访问,适合下载服务器,默认关闭
upstream { ##负载均衡配置
...
}
server { ##服务器级别,每一个server类似于httpd中的一个<VirtualHost,通俗来说就是一个网站>
listen 80;
server_name localhost;
location / { ##请求级别,类似与htt中的<Location>,用于定义URL与本地文件系统的映射关系
root html;
index index.html index.htm;
}
}
}keepalive_timeout 设置单个http请求最长的连接时长,单位为s;
该值设置过小可能会对大文件上传造成影响,导致文件上传失败
设置过大则会引起部分无效的http连接无法释放
nginx文件缓存
expires设置缓存过期时间
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10location ~ .*\.(gif|jpg|jpeg|png|bmp|swf)$ {
#过期时间为30天,
#图片文件不怎么更新,过期可以设大一点,
#如果频繁更新,则可以设置得小一点。
expires 30d;
}
location ~ .*\.(js|css)$ {
expires 10d;
}Cache-control:通过add_header来设置
no-store
彻底禁用缓冲,所有内容都不会被缓存到缓存或临时文件中。
no-cache
在浏览器使用缓存前,会往返对比ETag,如果ETag没变,返回304,则使用缓存。
public
所有内容都将被缓存(客户端和代理服务器都可缓存)
private
内容只缓存到私有缓存中(仅客户端可以缓存,代理服务器不可缓存)
max-age=xxx
缓存的内容将在 xxx 秒后失效,这个选项只在HTTP1.1可用,并如果和Last-Modified一起使用时,优先级较高。
1
2
3
4
5location / {
index index.html;
try_files $uri $uri/ /index.html;
add_header Cache-Control no-cache;
}
server指令可定义一个虚拟主机
1
2
3
4
5server {
listen $port; // 定义虚拟主机端口
server_name $server_name; // 服务名称
root $root_dir; // 根目录
}location区段:与客户端返回的URI进行匹配,匹配成功后进入location配置中处理请求
语法:location 修饰符 pattern {}
无修饰符,以指定模式开头进行匹配
1
location /aaa {}
= 修饰符,精确匹配
1
location = /aaa {}
~ 修饰符,正则表达式区分大小写
1
location ~ /aaa {}
~* 修饰符,正则表达式不区分大小写
1
location ~* /aaa {}
3. nginx配置
前后端分离部署
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17server {
listen 8082;
server_name dt-con-paltform-front;
root /dtstack/front/dt-con-platform-front/dist;
location / {
index index.html;
try_files $uri $uri/ /index.html;
}
location /api/v1/front/ {
proxy_pass http://172.16.8.194:8006;
}
location /v3/place/ {
proxy_pass http://restapi.amap.com;
}
}负载均衡
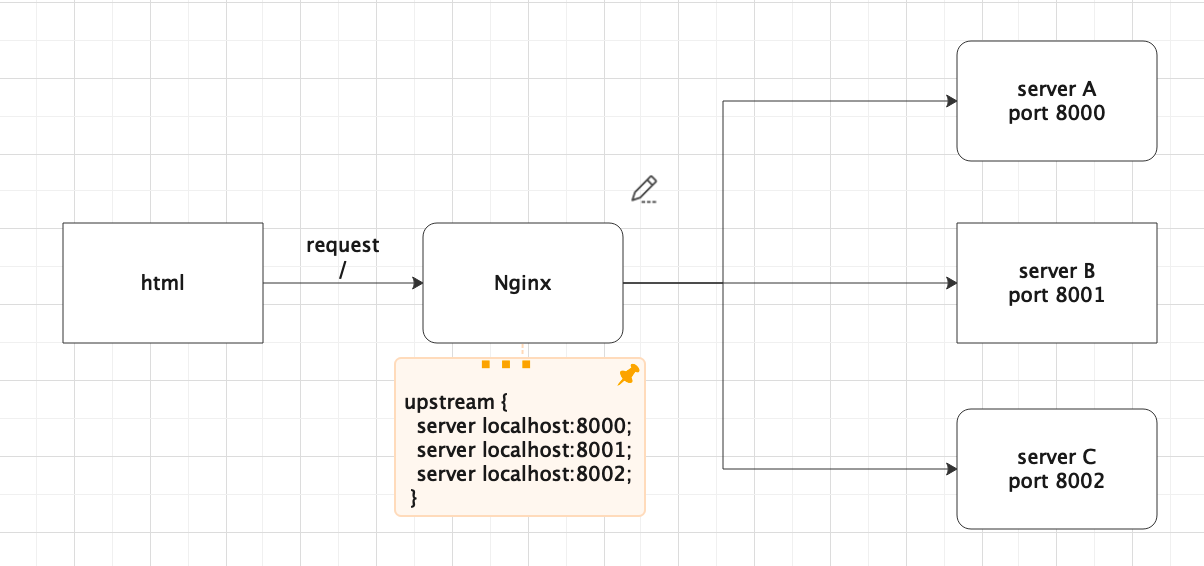
负载均衡优缺点
缺点:需要占用一定数量的服务器资源
优点:提高系统的稳定性
- 分发前端请求,减少单个后端服务的负载量
- 单台服务器挂掉了,不影响系统整体功能的使用
负载均衡请求分发机制:
轮询
每个请求按时间顺序逐一分配到不同的后端服务器,如果后端服务器down掉,能自动剔除
服务器权重
weight权重,权重越大,表示访问几率越大,用于后端服务器性能不均的情况
ip_hash
对ip进行hash处理,同一个ip发出的请求被分发到固定的服务器,可以解决后端session问题
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13upstream loader-server {
server localhost:8000;
server localhost:8001;
server localhost:8002;
}
server {
listen 8004;
server_name loader;
location / {
proxy_pass http://loader-server;
}
}