二叉搜索树
0 条评论二叉搜索树(Binary Search Tree)
二叉搜索树的定义:
二叉查找树,是指一棵空树或者具有下列性质的二叉树:
- 若任意节点的左子树不空,则左子树上所有节点的值均小于它的根节点的值;
- 若任意节点的右子树不空,则右子树上所有节点的值均大于它的根节点的值;
- 任意节点的左、右子树也分别为二叉查找树;
首先,先来看一个二叉搜索树的例子,认识一下什么样的树是一棵二叉搜索树:
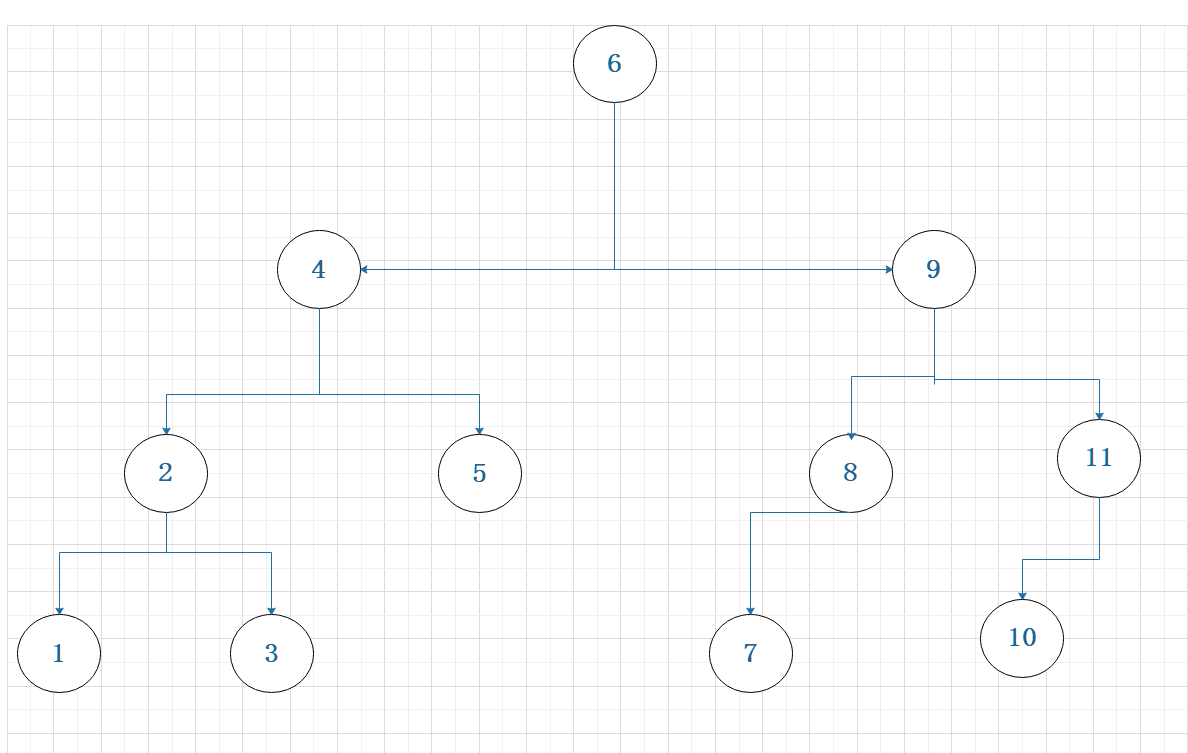
对于二叉树中的每一棵子树,其左子树中的所有节点key值都小于根节点;其右子树中的所有节点key值均大于根节点
注:为简化问题,暂时不考虑子树中key值相同的节点,即默认二叉树中key值是惟一的
二叉搜索树的中序遍历
1 | class TTreeNode<DataType> { |
二叉树的中序遍历
(递归版本)
1 | void in_order(root) { |
(迭代版本:借用栈实现)
1 | function in_order(root) { |
DFS
- Pre-order
- In-order
- Post-order
BFS
二叉搜索树的操作
- 二叉搜索树节点类型声明
1 | class TreeNode<DataType> { |
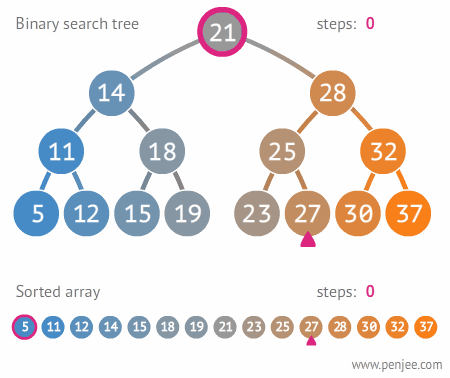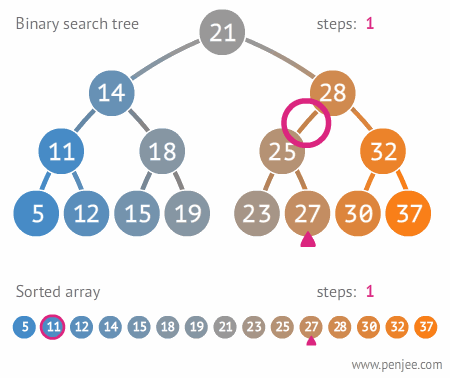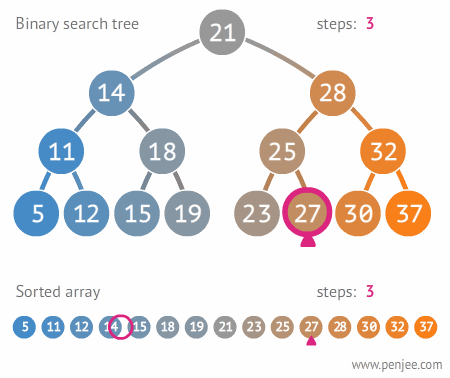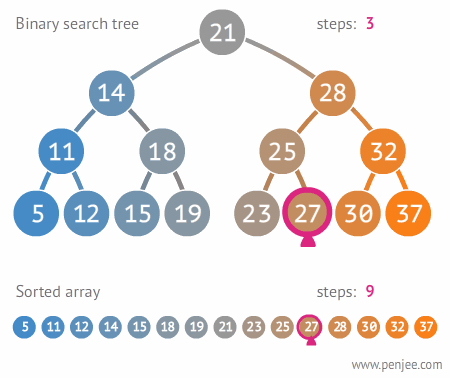
搜索
- 在二叉搜索树中根据给定关键字key查找节点:
- 从二叉搜索树的根节点开始进行比较
- 若节点的key值与给定的key值相等,查询成功,搜索结束
- 若给定的key值大于节点的key,则对右子树进行搜索;反之,对左子树进行搜索
- 当节点为null时,仍未匹配key值,则查询失败,搜索结束
1 | class BinarySearchTree<DataType> { |
插入
给定一个key值和value构成的节点,将节点插入二叉搜索树中,使得插入完成后的树依然是一棵二叉搜索树
与搜索的逻辑类似,只不过需要新增一个父节点指针
1 | class BinarySearchTree<DataType> { |
节点的前驱和后继
在聊二叉搜索树的删除之前,需要了解一个比较重要的概念,二叉搜索树节点的前驱节点和后继节点
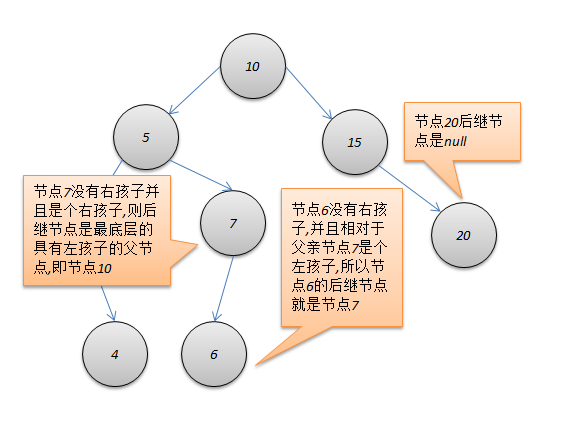
后继节点
如果节点存在右子树,则后继节点是右子树中的key值最小的节点
如果节点不存在右子树,则要向上层节点回溯,找到一个父级节点,使得node节点在父级节点的左子树中;
若未找到满足条件的父级节点,则说明node节点是最右侧的节点(搜索树最大节点),则不存在后继节点
1 | class BinarySearchTree<DataType> { |
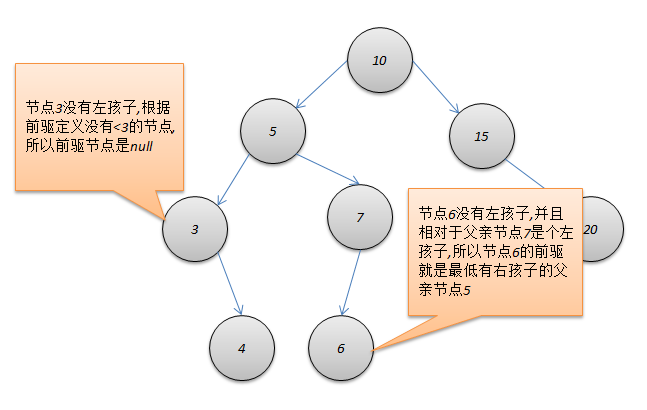
前驱节点
如果节点存在左子树,则后继节点是左子树中的key值最大的节点
如果节点不存在左子树,则要向上层节点回溯,找到一个父级节点,使得node节点在父级节点节点的右子树中;
若未找到满足条件的父级节点,则说明node节点是最左侧的节点(搜索树最小节点),则不存在后继节点
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31class BinarySearchTree<DataType> {
root: TreeNode<DataType> = null;
// 计算节点的前驱节点
_prev(node: TreeNode<DataType>): TreeNode<DataType> {
if (node === null) return null;
if (node.left !== null) {
// node存在左子树
return this._max(node.left);
} else {
// node不存在左子树
let ptr = node;
while(ptr.parent !== null && ptr.parent.left === ptr) {
ptr = ptr.parent;
}
return ptr.parent;
}
}
// 查找某一棵二叉搜索树的key值最大的节点
// 不断搜索右子树,直到最右侧节点,极为key值最大节点
_max(node: TreeNode<DataType>): TreeNode<DataType> {
let ptr = node;
let p = null;
while(ptr !== null) {
p = ptr;
ptr = ptr.right;
}
return p;
}
...
}
删除
二叉树节点的删除
给定一个key值,从二叉搜索树中删除对应节点,需要保证删除后的二叉树依然是一棵二叉搜索树
节点删除比较复杂,需要分为以下三种情况:
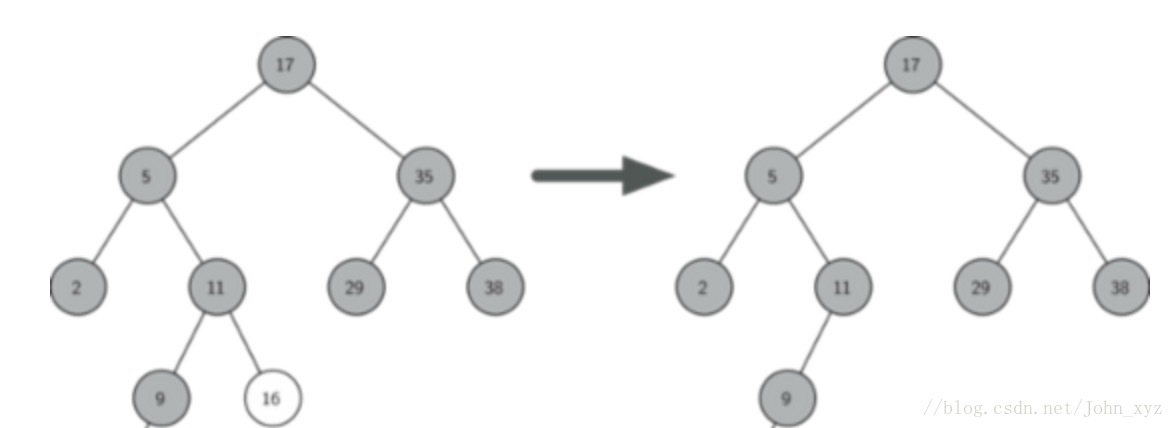
CASE 1:
待删除节点Z没有孩子节点,即Z为叶子节点,直接删除节点,重置parent指针
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11if (target.isLeafNode()) {
// 目标节点没有子节点的情况
if (target.isRoot()) {
this.root = null;
} else {
const flag = target.isLeftChild() ? 'left' : 'right';
target.parent[flag] = null;
target.parent = null;
}
return true;
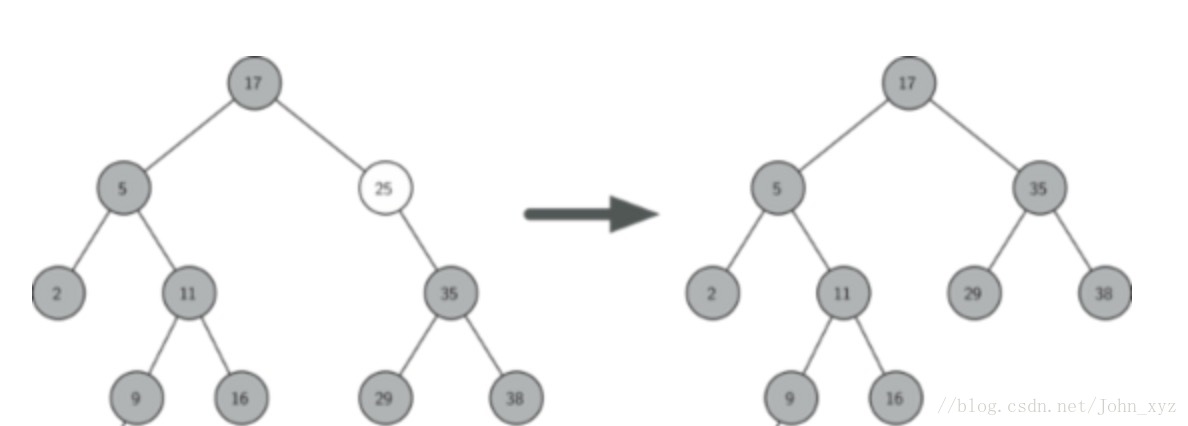
}CASE 2:
待删除节点Z有且仅有一个子节点,则将Z节点删除,用Z节点的子节点取代原先的Z节点,更新parent指针
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15// CASE 2
// 有且仅有左子节点或者右子节点
const targetFlag = target.left === null ? 'right' : 'left';
const targetParent = target.parent;
if (target.isRoot()) {
// 根节点
this.root = target[targetFlag];
} else {
const parentFlag = target.isLeftChild() ? 'left' : 'right';
const parent = target.parent;
parent[parentFlag] = target[targetFlag];
}
target[targetFlag].parent = targetParent;
target.reset();CASE 3:
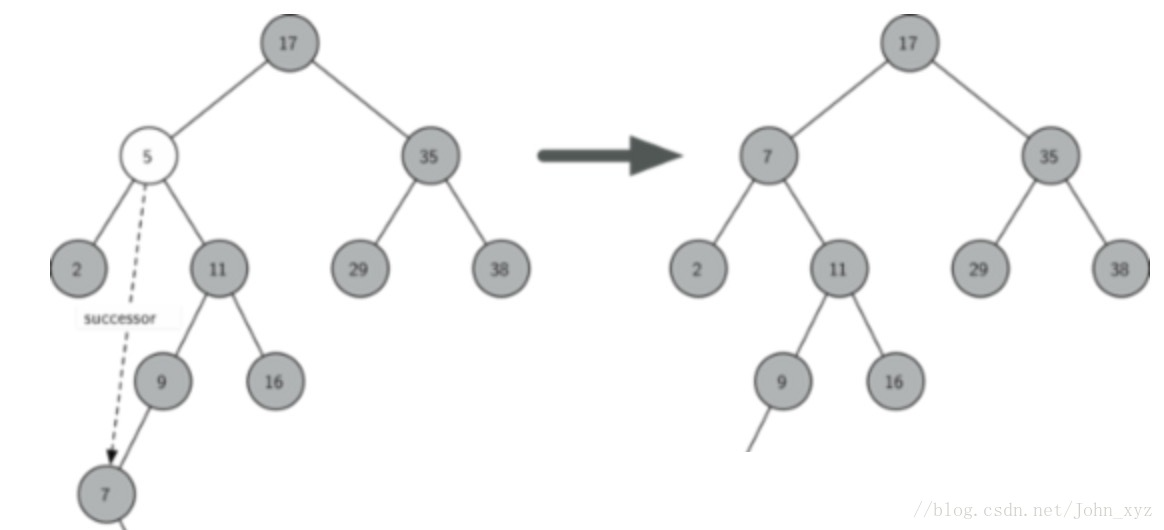
待删除节点Z有两个子节点,此时删除Z节点后有两种策略:
- 策略一:从左子树中找出key值最大的节点(即节点Z的前驱节点),取代删除的节点Z
- 策略二:从右子树中找出key值最小的节点(即节点Z的后继节点),取代删除的节点Z
(主要目标是从Z节点的所有子节点中找出一个节点,满足这个节点的key比所有左子树中的key要大,比右子树中的key要小。)
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21else if(target.left !== null && target.right !== null) {
// CASE 3
const next = this._next(target);
// 释放next节点的父节点指针
const flag = next.isLeftChild() ? 'left' : 'right';
next.parent[flag] = next.right;
if (target.isRoot()) {
this.root = next;
} else {
const parentFlag = target.parent.left === target ? 'left' : 'right';
target.parent[parentFlag] = next;
}
next.left = target.left;
next.right = target.right;
next.parent = target.parent;
target.left && (target.left.parent = next);
target.right && (target.right.parent = next);
target.reset();
return true;
}
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56delete(key: number): boolean {
const target = this.find(key);
if (target === null) return false;
if (target.isLeafNode()) {
// CASE 1
// 目标节点没有子节点的情况
if (target.isRoot()) {
this.root = null;
} else {
const flag = target.isLeftChild() ? 'left' : 'right';
target.parent[flag] = null;
target.parent = null;
}
return true;
} else if(target.left !== null && target.right !== null) {
// CASE 3
const next = this._next(target);
if (next.isLeftChild()) {
next.parent.left = null;
} else {
next.parent.right = null;
}
if (target.isRoot()) {
this.root = next;
} else {
const parentFlag = target.parent.left === target ? 'left' : 'right';
target.parent[parentFlag] = next;
}
next.left = target.left;
next.right = target.right;
next.parent = target.parent;
target.left && (target.left.parent = next);
target.right && (target.right.parent = next);
target.reset();
return true;
} else {
// CASE 2
// 有且仅有左子节点或者右子节点
const targetFlag = target.left === null ? 'right' : 'left';
const targetParent = target.parent;
if (target.isRoot()) {
// 根节点
this.root = target[targetFlag];
} else {
const parentFlag = target.isLeftChild() ? 'left' : 'right';
const parent = target.parent;
parent[parentFlag] = target[targetFlag];
}
target[targetFlag].parent = targetParent;
target.reset();
return true;
}
}
二叉搜索树问题及优化
二叉搜索树的算法复杂度
| 操作 | 复杂度 |
|---|---|
| 搜索 | O(h) |
| 插入 | O(h) |
| 删除 | O(h) |
上述描述的复杂度中h二叉搜索树的高度,( log n < h < n) 二叉搜索树的弊端在于其没有自平衡策略
最终二叉搜索树构建的过程中,受到输入数据的影响会导致二叉搜索的畸形
WORST CASE:
考虑初始化数据为以下数据:
1, 2, 3 ,4 ,5 ,6 ,7 ,8, 9, 10
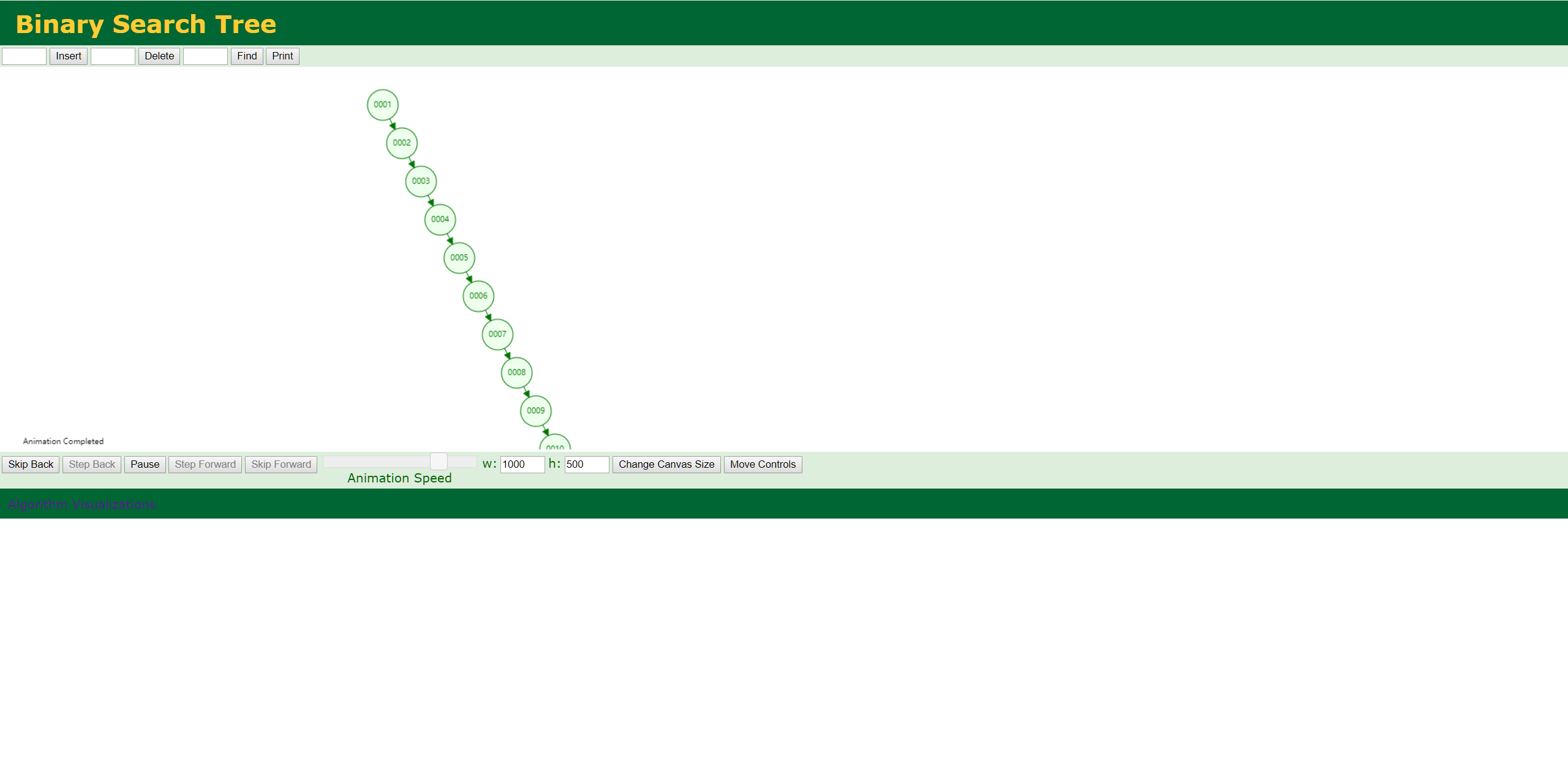
在这种状况下,二叉搜索树与链表几乎没有区别,无论是搜索,插入还是删除,其复杂度均达到了O(n)
https://www.cs.usfca.edu/~galles/visualization/BST.html
随机化算法
随机化算法 + 二叉搜索树
给定一组数据[1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8 ,9, 10],根据给定的数组构建一棵二叉搜索树
朴素顺序算法,会按照给定数据顺序生成二叉搜索树
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8const list = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10];
const bst = new BinarySearchTree<string>();
for(let n of list) {
bst.insert(n, `data-${n}`);
}随机化算法
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9const list = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10];
const bst = new BinarySearchTree<string>();
while(list.length > 0) {
const random = Math.floor(Math.random() * (list.length - 1));
const item = list.splice(random, 1);
console.log(item, random);
bst.insert(item[0], `data-${item}`);
}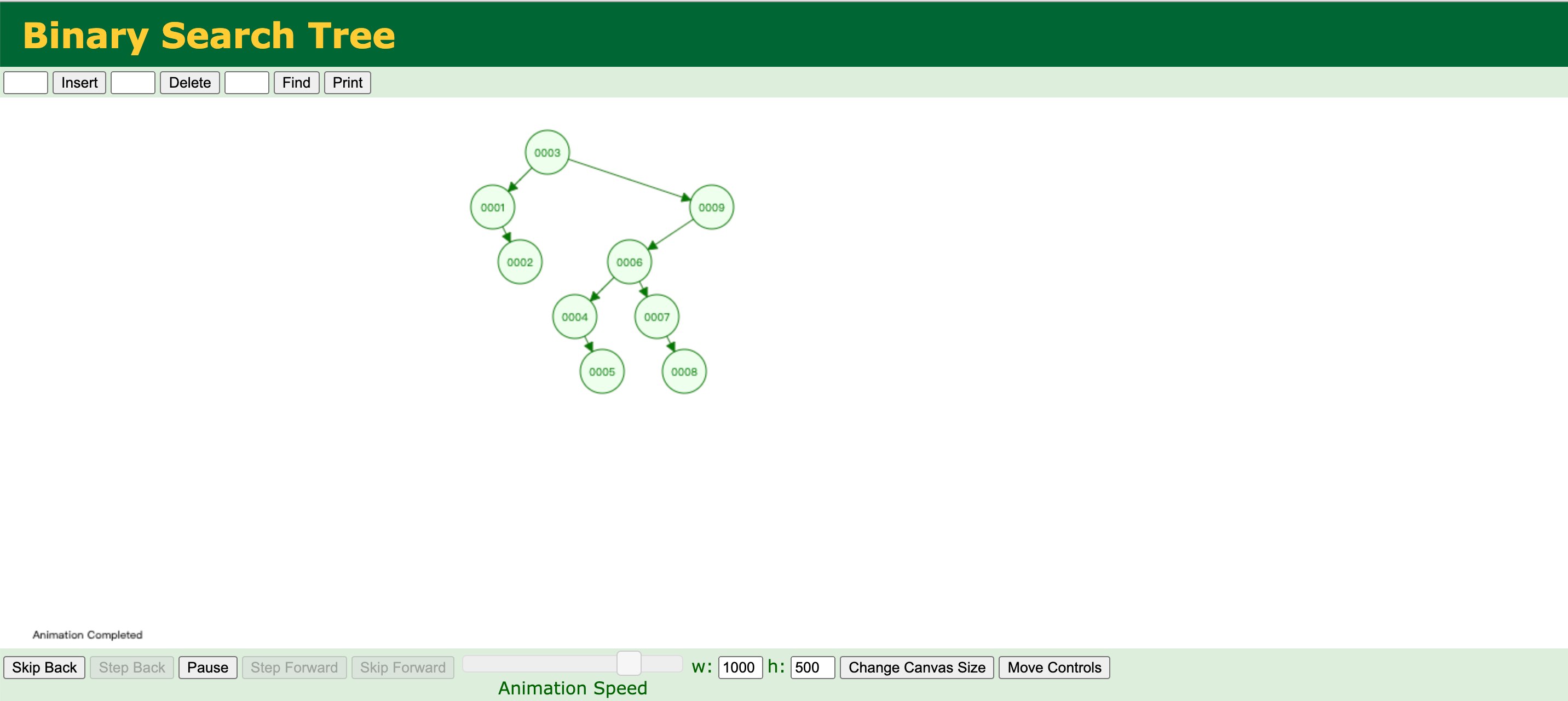
随机化构建二叉搜索树,仅仅对于二叉树的初始化阶段是有效的,对于初始化完成后的插入与删除阶段是没有优化作用的
后续二叉树的插入和删除操作依然会导致二叉树的畸形
随机化算法 + 快速排序